深入理解 Spark Partitioning
RDD是一个大型的数据项集合。在我们的大数据处理中,这种大型数据项集合在单机环境下是放不下的,因此,它们被划分在多个节点上。当然,RDD的分区操作是由Spark自动完成的。
RDD Partitioning 属性
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| partitions | returns an array with all partition references of source RDD |
| partitions.size | gives number of partitions of source RDD |
| partitioner | returns Partitioner if any, HashPartitioner, RangePartitioner,CustomPartitioner. |
| defaultParallelism | returns default level of parallelism defined on SparkContext.By default it is number of cores available to application. |
Spark用RDD的partitioner来决定分区算法。如果partitioner为None的话,则随机均等分区
影响 Partitioning 的因素
- 可用资源 - CPU cores
- 外部数据源 - 本地的collections、Cassandra table 或 HDFS file的数量决定分区数
- 生成RDD的Transformations操作
Block、Task 和 Partition 的关系
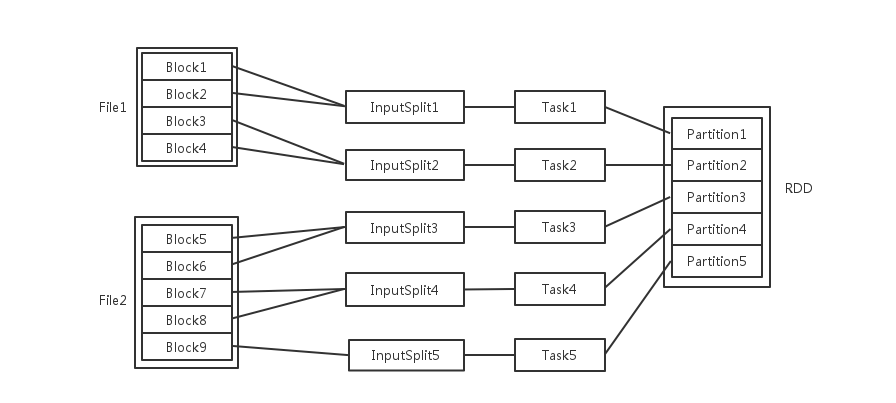 输入可能以多个文件的形式存储在HDFS上,每个File都包含了很多块,称为Block。
输入可能以多个文件的形式存储在HDFS上,每个File都包含了很多块,称为Block。
当Spark读取这些文件作为输入时,会根据具体数据格式对应的InputFormat进行解析,一般是将若干个Block合并成一个输入分片,称为InputSplit,注意InputSplit不能跨越文件。
随后将为这些输入分片生成具体的Task。InputSplit与Task是一一对应的关系。
随后这些具体的Task每个都会被分配到集群上的某个节点的某个Executor去执行。
- 每个节点可以起一个或多个Executor。
- 每个Executor由若干core组成,每个Executor的每个core一次只能执行一个Task。
- 每个Task执行的结果就是生成了目标RDD的一个partiton。
注意:这里的core是虚拟的core而不是机器的物理CPU核,可以理解为就是Executor的一个工作线程。
而 Task被执行的并发度 = Executor数目 * 每个Executor核数。
至于partition的数目:
- 对于数据读入阶段,例如sc.textFile,输入文件被划分为多少InputSplit就会需要多少初始Task。
- 在Map阶段partition数目保持不变。
- 在Reduce阶段,RDD的聚合会触发shuffle操作,聚合后的RDD的partition数目跟具体操作有关,例如repartition操作会聚合成指定分区数,还有一些算子是可配置的。
默认Partitioning操作
默认的分区操作取决于RDD是如何创建的,比如创建于外部数据源,像Cassandra table, HDFS file等,或者通过transforming从另一个RDD转化而来
| API Call | partitions.size | partitioner |
|---|---|---|
| sc.parallelize(…) | sc.defaultParallelism | NONE |
| sc.cassandraTable(…) | sc.defaultParallelism or data-size/64 MBs , whichever is greater | NONE |
| sc.textFile(…) | sc.defaultParallelism or number of file blocks , whichever is greater | NONE |
| filter(),map(),flatMap(),distinct() | same as parent RDD | NONE except filter preserve parent RDD’s partitioner |
| rdd.union(otherRDD) | rdd.partitions.size + otherRDD. partitions.size | NONE |
| rdd.intersection(otherRDD) | max(rdd.partitions.size, otherRDD. partitions.size) | NONE |
| rdd.subtract(otherRDD) | rdd.partitions.size | NONE |
| rdd.cartesian(otherRDD) | rdd.partitions.size * otherRDD. partitions.size | NONE |
| reduceByKey(),foldByKey(),combineByKey(),groupByKey() | same as parent RDD | HashPartitioner |
| sortByKey() | same as parent RDD | RangePartitioner |
| mapValues(),flatMapValues() | same as parent RDD | parent RDD’s partitioner |
| cogroup(), join(), ,leftOuterJoin(), rightOuterJoin() | depends upon certain input properties of two RDDs involved. | HashPartitioner |
多少个分区比较好?
拥有太少或太多分区数,都有明显的优缺点。因此,建议根据集群的配置和需求来谨慎选择。
分区数太少的缺点:
- 并发少 - 没有充分地利用并发性,有些工作节点空闲出来
- 数据倾斜和不恰当的资源利用 - 如果数据在某个分区发生倾斜,造成该工作节点的计算任务远大于其他节点,进而出现资源问题
分区数太多的缺点:
- 任务的调度时间可能会超过实际执行时间
推荐的分区规则:
- 一般来说分区数在100-100000之间,取决于集群的大小和数据
- 下限 - cores的2倍
- 上限 - 每个task的执行时间最好在100+ms,如果执行时间过短,说明分区数据量太小,程序将花费更多的时间在调度任务上
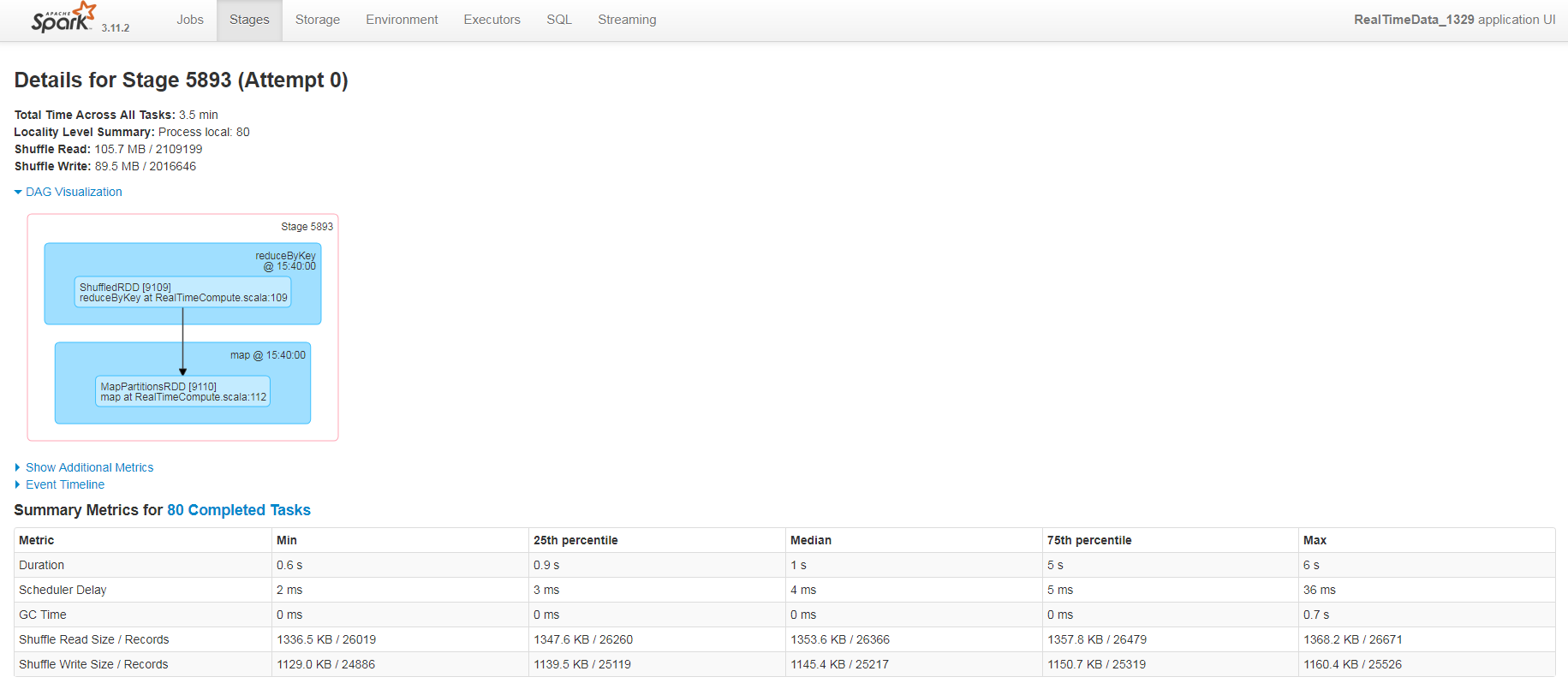
我们可以调试分区参数并在Spark Application UI上监控执行和调度时间,从而把程序调到更优
优化总结
API
Task被执行的并发度 = Executor数目 * 每个Executor核数
Task与Partition一一对应,Partition数最好为并发度的2~3倍。因此最好设置 spark.default.parallelism = executors * cores * 2
外部数据源
Spark 程序
当从HDFS读文件时, 默认的 spark.hadoop.mapred.max.split.size = 269000000(256MB)
而实际的Split size = max(mapred.min.split.size, min(mapred.max.split.size, dfs.block.size))
因此,当读取操作需要提升并行度时,可以调低 mapred.max.split.size ,比如16MB;反之亦然。
Spark Streming 程序
spark.streaming.blockInterval 这个参数用来设置Spark Streaming里Stream Receiver生成Block的时间间隔,默认为200ms。
具体的行为表现是:Receiver所接收的数据,每隔这里设定的时间间隔,就从Buffer中生成一个StreamBlock放进队列,等待进一步被存储到BlockManager中供后续计算过程使用。理论上来说,为了每个Streaming Batch 间隔里的数据是均匀的,这个时间间隔当然应该能被Batch的间隔时间长度所整除。
每个Receiver 产生的的input-block数为: batchInterval * 1000 / blockInterval
因此,建议 blockInterval = Receivers * batchInterval * 1000 / Parallelism,这样下来,每个batch产生的StreamBlock数:
StreamBlocks = Receivers * batchInterval * 1000 / blockInterval = Receivers * batchInterval * 1000 / (Receivers * batchInterval * 1000 / Parallelism) = Parallelism
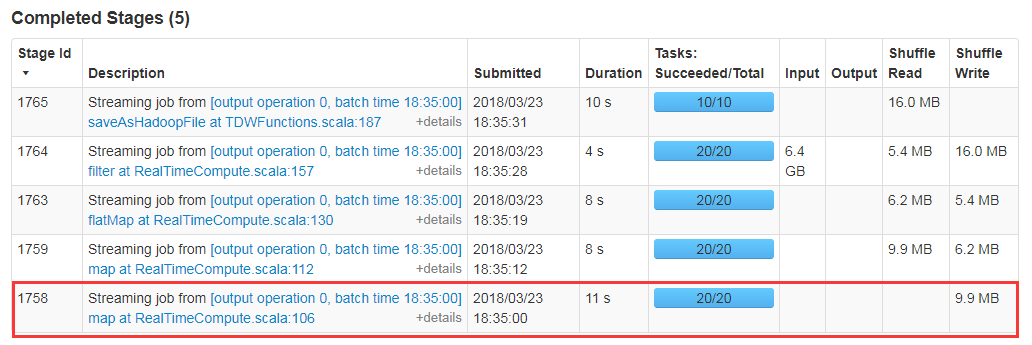
优化前:spark.streaming.blockInterval 取默认值,partition和task数太多
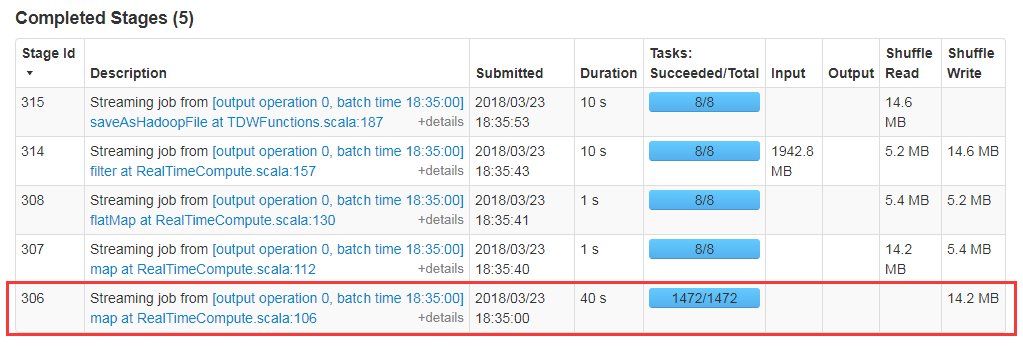
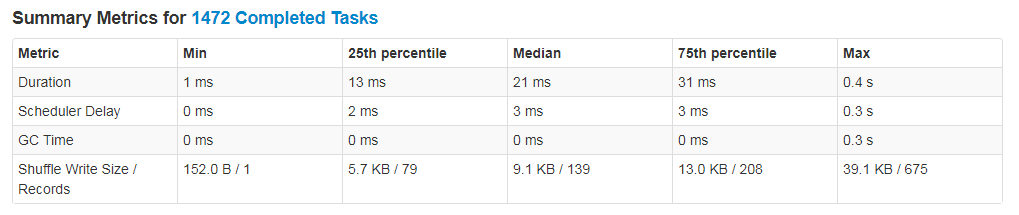
优化后:设置spark.streaming.blockInterval = Receivers * batchInterval * 1000 / Parallelism,分区数明显变少,执行效率大大提高